Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a general term for all disorders of the retina caused by diabetes. There are two major stages of retinopathy: non-proliferative and proliferative.
- Non-proliferative retinopathy
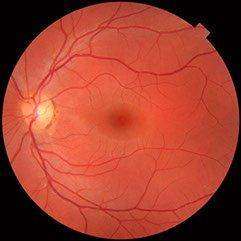
In nonproliferative retinopathy, the most common form of retinopathy, capillaries in the back of the eye balloon and form pouches called Microaneurysms. Non-proliferative retinopathy can move through three stages (mild, moderate, and severe), as more and more blood vessels become blocked.
Although retinopathy does not usually cause vision loss at this stage, the blood vessels become leaky. When the macula swells with fluid, a condition called macula edema, vision blurs and can be lost entirely. Although nonproliferative retinopathy usually does not require treatment, macular edema must be treated, but fortunately treatment is usually effective at stopping and sometimes reversing vision loss.
- Proliferative Retinopathy
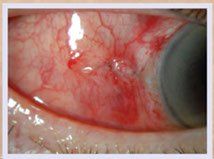
In some people, retinopathy progresses after several years to a more serious form called proliferative retinopathy. In this form, the blood vessels are so damaged they close off. In response, new blood vessels start growing in the retina. These new vessels are weak and can leak blood, blocking vision, which is a condition called vitreous hemorrhage. The new blood vessels can also cause scar tissue to grow. After the scar tissue shrinks, it can distort the retina or pull it out of place, a condition called retinal detachment.
Your retina can be badly damaged before you notice any change in vision. Most people with non-proliferative retinopathy have no symptoms. Even with proliferative retinopathy, the more dangerous form, people sometimes have no symptoms until it is too late to treat them. For this reason, you should have your eyes examined regularly by an eye care professional.
Am I at risk for retinopathy?
Several factors influence whether you get retinopathy:
• blood sugar control
• blood pressure levels
• how long you have had diabetes
• genes
The longer you've had diabetes, the more likely you are to have retinopathy. Almost everyone with type 1 diabetes will eventually have nonproliferative retinopathy. And most people with type 2 diabetes will also get it. But the retinopathy that destroys vision, proliferative retinopathy, is far less common.
People who keep their blood sugar levels closer to normal are less likely to have retinopathy or to have milder forms.
Symptoms and Detection:
Many times, patients report no symptoms in the early stage of Diabetic Retinopathy. Patients experience following symptoms in the advance stage of this eye condition:
• Fluctuating vision
• Eye floaters and spots
• Development of a scotoma or shadow in your field of view
• Blurry and/or distorted vision
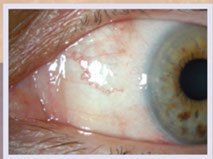
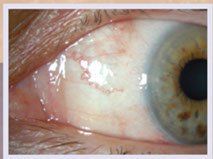
• Corneal abnormalities such as slow healing of wounds due to corneal abrasions
• Double vision
• Eye pain
• Near vision problems unrelated to presbyopia
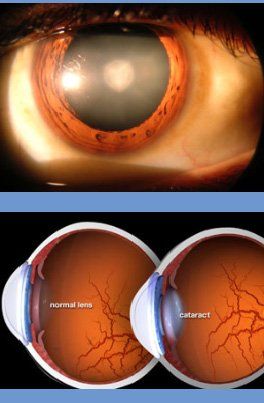
• Cataracts
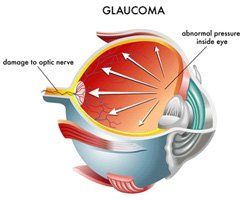
The irregular growth of new blood vessels gives rise to serious complications such as retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, glaucoma and blindness. Usually, this disease affects both eyes.
How is it treated?
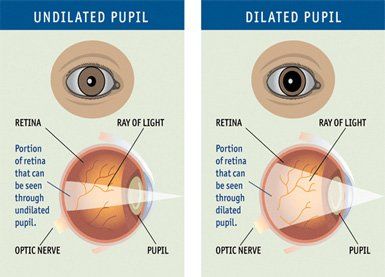
Huge strides have been made in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Treatments such as scatter photocoagulation, focal photocoagulation, and vitrectomy prevent blindness in most people. The sooner retinopathy is diagnosed, the more likely these treatments will be successful. The best results occur when sight is still normal.
- In photocoagulation, the eye care professional makes tiny burns on the retina with a special laser. These burns seal the blood vessels and stop them from growing and leaking.
- In scatter photocoagulation (also called panretinal photocoagulation), the eye care professional makes hundreds of burns in a polka-dot pattern on two or more occasions. Scatter photocoagulation reduces the risk of blindness from vitreous hemorrhage or detachment of the retina, but it only works before bleeding or detachment has progressed very far. This treatment is also used for some kinds of glaucoma.
- Side effects of scatter photocoagulation are usually minor. They include several days of blurred vision after each treatment and possible loss of side (peripheral) vision.
- In focal photocoagulation, the eye care professional aims the laser precisely at leaking blood vessels in the macula. This procedure does not cure blurry vision caused by macular edema. But it does keep it from getting worse.
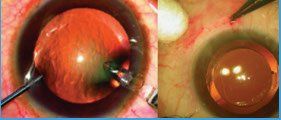
- When the retina has already detached or a lot of blood has leaked into the eye, photocoagulation is no longer useful. The next option is vitrectomy, which is surgery to remove scar tissue and cloudy fluid from inside the eye. The earlier the operation occurs, the more likely it is to be successful. When the goal of the operation is to remove blood from the eye, it usually works. Reattaching a retina to the eye is much harder and works in only about half the cases.